A photo taken in the Laboratory of Micro- and Nanotomography, at the Faculty of Physics and Applied Computer Science; Photo: AGH UST
In total, there are more than 800 laboratories at the AGH UST. At 16 faculties and extra-faculty units, our scientists work daily with special equipment, often unique in Poland or Europe. For Fat Thursday, AGH UST employees and students, using the rich laboratory base of the university, took a closer look at the doughnuts. To analyse them, they used, among other things, microscopes, CT scanners, grinders, and laser scanning technology.
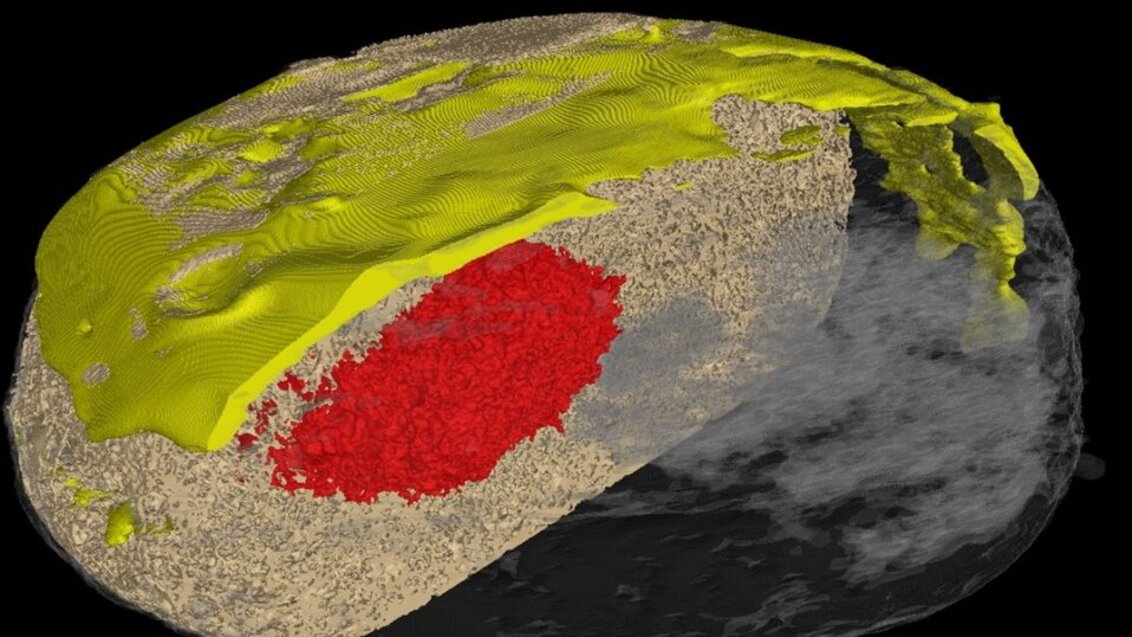
The effects of unorthodox investigations into the inner structure of doughnuts
The AGH UST laboratories are used mainly to carry out environmental surveys, physical and chemical analyses, and measurements of microstructure parameters. Using the equipment at the university, our students examine materials on the nano scale and investigate the behaviour of the materials under the influence of various levels of load.
Access to the laboratories allows our scientists to conduct research commissioned by industry in general, including the energy, automotive, and aviation branches. The following centres conduct research that is unique in Poland:
- International Centre of Electron Microscopy for Materials Science by the Faculty of Metals Engineering and Industrial Computer Science. It possesses one of the most powerful electron microscopes in the world – the Titan Cubed. The device is used to perform microanalyses on the atomic scale.
- Anechoic chamber located at the Faculty of Mechanical Engineering and Robotics in the Laboratory of Technical Acoustics, where the level of background acoustic pressure measured during the day is 1.5 decibels (dBA), whereas at night it drops even below 0 dBA.
- Research for the benefit of science, especially in the field of computer networks, large computing powers, and other ICT services, is conducted at the Academic Computer Centre CYFRONET which is home to Athena – currently the fastest supercomputer in Poland.
- The Academic Centre for Materials and Nanotechnology carries out interdisciplinary research in the field of modern engineering, physics, material chemistry, nanodiagnostics, and nanotechnology. The Centre comprises six research lines and four research teams that conduct fundamental and application research on metallic, semiconductor, magnetic, and polymer materials, including their composites and nanostructures. In particular, the unit focuses on using electron microscopy in its investigations.
- Centre of Energy – is a research unit focused on developing power technologies, including conventional energy, fuels and sorbents, renewable energy sources: wind, water, hydrogen, photovoltaics, biomass, and biogas, as well as waste fuel and power grids.
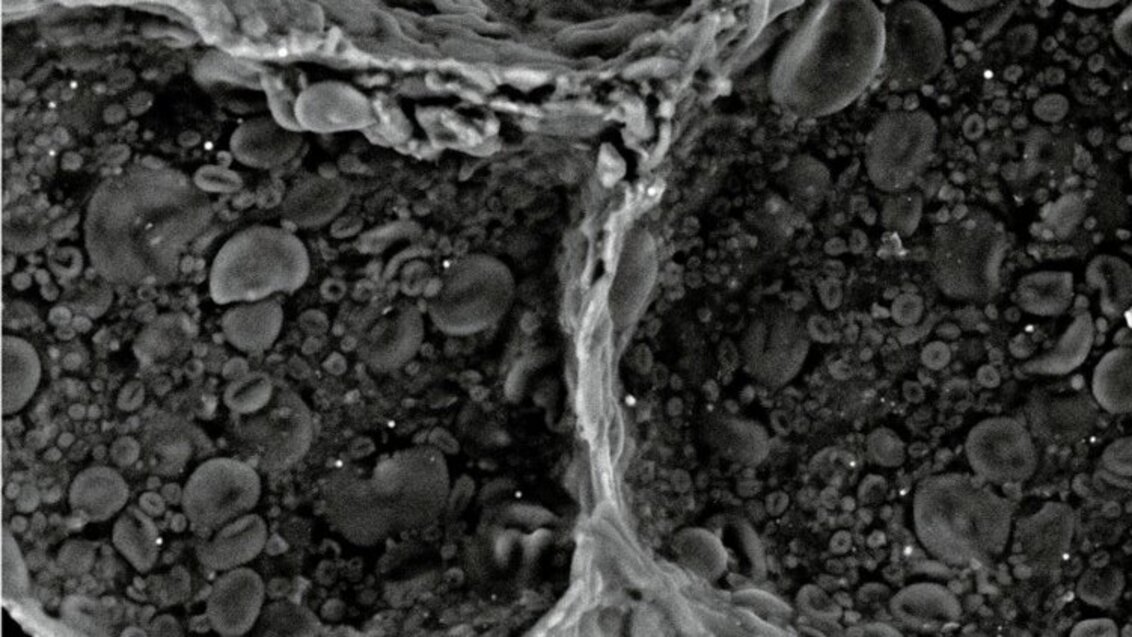
The interior of a doughnut with a +400 magnification. Observation made with the FEI Quanta 200 FEG scanning electron microscope. Laboratory of Organic Geochemistry and Environmental Surveys, Faculty of Geology, Geophysics, and Environmental Protection. Photo: AGH UST
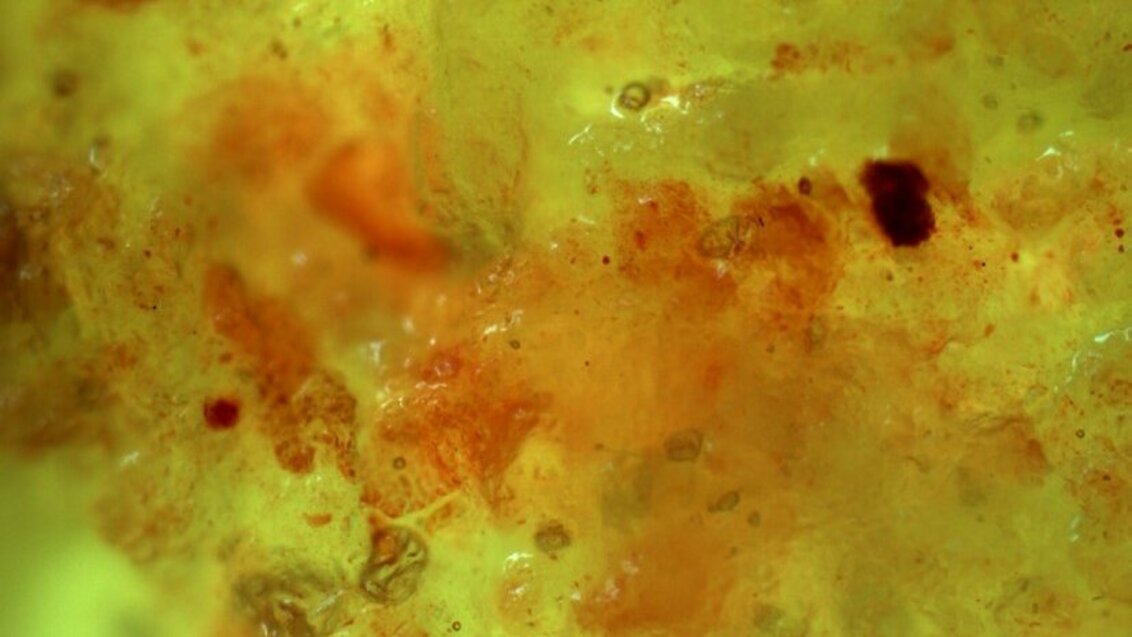
A photo taken using a ZEISS Axiolab 5 polarising transmitted light microscope at the Faculty of Drilling, Oil, and Gas. Photo: AGH UST
 Pre-election meeting with a candidate for the position of rector
Pre-election meeting with a candidate for the position of rector  Agreement on cooperation with OPAL-RT
Agreement on cooperation with OPAL-RT  Krakow DIANA Accelerator consortium members with an agreement
Krakow DIANA Accelerator consortium members with an agreement  Meeting with the Consul General of Germany
Meeting with the Consul General of Germany  More Academic Sports Championships finals with medals for our students
More Academic Sports Championships finals with medals for our students  Bronze for our swimmers at Academic Championships
Bronze for our swimmers at Academic Championships  Smart mountains. AGH University scholar develops an intelligent mountain rescue aid system
Smart mountains. AGH University scholar develops an intelligent mountain rescue aid system